Explore the architectural features of the Quazar family of products from MoSys in this Part 1 introduction by Mark Baumann, Director or Product Definition & Applications at MoSys, Inc.
In Part I of this blog, we will be exploring the architectural features of the newly announced Quazar family of products from MoSys. The Quazar family are groups of parts that are designed to address the needs for the next generation of Synchronous SRAM devices on the market. Quad Data Rate (QDR) devices currently have the largest share of this market.
As MoSys approached this issue, it was realized that there are some features and goals to address with the present QDR devices. In reviewing the present QDR devices that are on the market, the issues were:
- • Density of 144Mb with one offering at 288Mb
- • Use of wide parallel busses that run at very high frequency
- • Strict rules to layout boards to accept these fast-wide busses
- • Sourced by multiple vendors (Cypress (Infineon) and GSI) but each vendor uses a slightly different pinout
- • No commitment to a future roadmap
In seeking to ensure that the new MoSys device addresses each of these issues the goals set out were:
- • Develop a device that is at least 576Mb in density
- • Use a bus structure that is available today and has a growth path to future speed and bandwidth (Since SerDes are becoming more ubiquitous on FPGAs, ASICs and ASSPs are considered a strong option)
- • Source – work on a guaranteed source of supply (continuity of supply agreement)
The design approach that MoSys is presenting, we believe, is a significant improvement over a standard QDR device. MoSys has architected a device that is 4 to 8 times the density of a QDR device and achieves this with comparable system latency and 2 to 5 times the system access bandwidth.
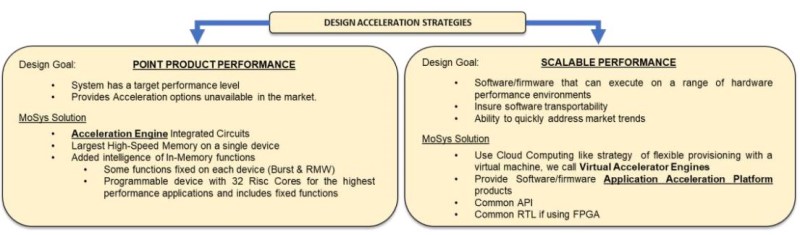
If you examine the MoSys Quazar family of devices, you will see that at many levels the architecture has been developed to support a list of feature goals. These being:
- • Cell design
- • Bank architecture
- • Partition architecture
- • Quad Partition structure
- • Internal Bus structure
- • Internal clocking and Trc
In Part 2, we’ll explore how each of these features support the goal of providing a next generation QDR replacement.
Ähnliches Produkt:
Ähnliches Produkt:
Ähnliches Produkt:



