The new IEEE 802.3bt Power over Ethernet (PoE) standard is a game-changer. With support for up to 90 W, PoE is now applicable to a wide range of higher power applications. Smart buildings employ many different types of smart devices – including industrial equipment, lighting, cameras, kiosks, monitors, scanners, and even small workstations – that have different power requirements (see Figure 1). Now, the power and connectivity needs of all of these devices can be met with a single technology.

Figure 1: The high power levels of IEEE 802.3bt Power over Ethernet enable a wide range of new applications and use cases, making it possible to for the power and connectivity needs of all of these devices to be met with using a single technology
PoE brings many advantages to high power smart building, industrial, and lighting applications. For applications that are running a network connection anyway, PoE eliminates the need to run an additional power cable. This simplifies installation, lowers CAPEX, and reduces OPEX as well. In addition, PoE centralizes backup power. This, in turn, enables continuous operation during power interruptions in a way not possible when devices are plugged into outlets throughout a building.
What’s more, PoE provides a means to bring intelligence to new applications, such as smart lighting. Now it is possible to power bigger systems, such as large digital signage combined with an advanced imaging system.
High Power, High Efficiency
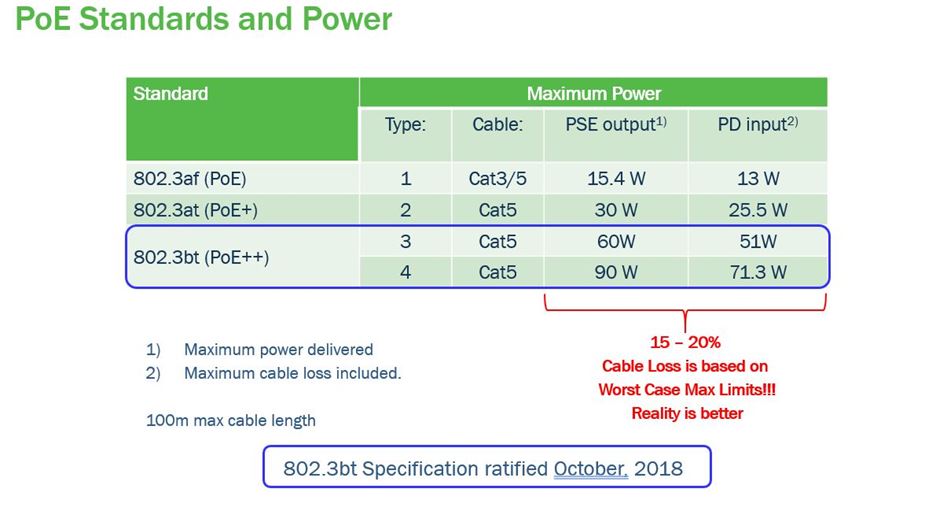
This table shows the evolution of PoE from 15 W to 30 W to 90 W
Table 1 shows the evolution of PoE from 15 W to 30 W to 90 W. The problem with running power is that efficiency is never 100%: Table 1 also shows the worst-case cable losses for a 100 m cable length. Depending upon the application, device in use, and cable being used, actual losses can be significantly lower. For example, in a recent smart building case study1, relative cable losses were just 2.68%, substantially lower than the projected worst-case efficiency of 15 – 20% (see Figure 2).
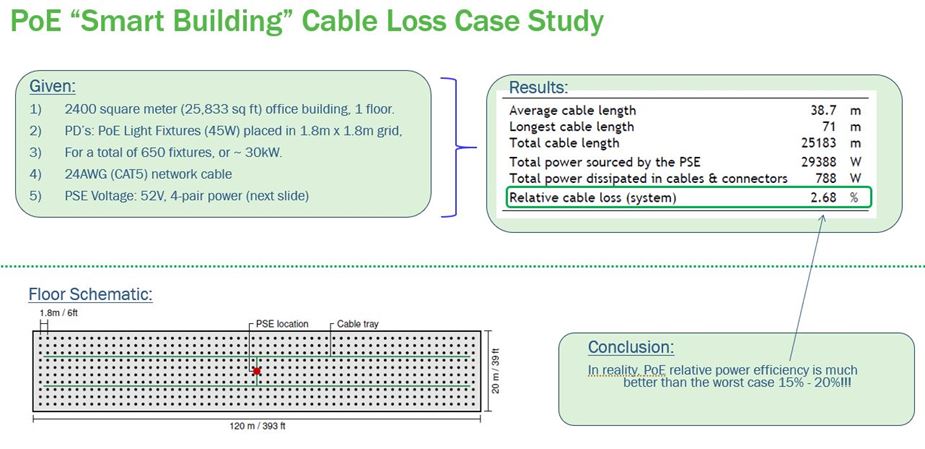
Figure 2: In a recent smart building case study2, relative cable losses were just 2.68%, substantially lower than the projected worst case efficiency of 15 – 20%
With the three stages of the standard, different application power requirements can be met efficiently. Because the standard is backwards compatible, devices built to operate on 802.3af (15.4 W) and 802.3at (30 W) can be connected to 802.3bt (90 W). This backwards compatibility enables 802.3bt to deliver significant benefits to PoE networks based on 802.3af and 802.at.
The 90 W capabilities of 802.3bt gives users more flexibility in consolidating PoE applications. Because the port can power all devices, installation and management of devices is simplified. In addition, if only 30 W is needed for a particular device, the extra available power (i.e., 60 W) can be routed to another port. Such flexibility reduces opportunities for human error (i.e., connecting a device to a switch that cannot supply enough power), resulting in more reliable – and more cost effective – infrastructure.
Another key benefit of 802.3bt is that users don’t have to worry as much about whether they are connecting a device that will overload the PoE network. This extra capacity translates to extra peace of mind.
This additional headroom, if you will, is also a boon to product designers. Because there’s more power coming down the chain, designers have more flexibility in their power budget. This translates to greater functionality, higher performance, and/or connecting more devices.
Finally, 802.3bt introduces Short Maintain Power Signature (Short MPS). Short MPS was designed for lighting applications that require a low standby power. So long as the powered device maintains a minimum current, it can keep its connection to the power source active. When the powered device is ready to draw more power, it can do so quickly, either using the power allocation already assigned to it or by requesting a new allocation from the available pool.
Worth noting: Other technologies fall short of PoE’s mark. USB, for example, is extremely limited by cable length and requires redrivers. PoE is also much easier to implement compared to USB.
Powered Device Interface Controllers
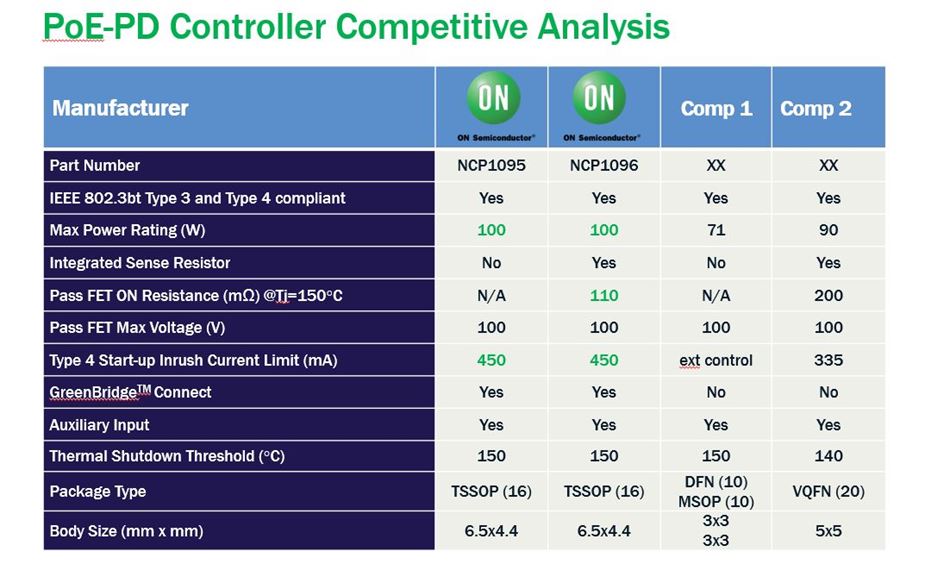
Figure 3: The NCP1095 and NCP1096 PoE Powered Device Interface Controllers offer industry-leading performance and efficiency
ON Semiconductor is a leader in PoE technology and one of the first companies to bring 802.3bt to market (see Figure 3). The NCP1095 PoE Powered Device Interface Controller is 802.3bt, 802.3af, and 802.3at compliant (backwards compatible), allowing for up to 90 W of power. It has an internal 70 mΩ pass transistor to support high-power applications and requires an external sense resistor and FET. The NCP1096 PoE Powered Device Interface Controller is also backwards compatible and allows for up to 100 W of power (see below). It has both an integrated hot swap FET and sense resistor.
Both devices support auto-classification (Autoclass), allowing power sourcing equipment to assign power to each connected powered device (PD) in an efficient manner. For example, devices can dynamically request a specific power level, either to get more power or to release power back to the pool. With Autoclass, the power source is able to assign a lower power than requested to accommodate more devices.
The NCP1095 and NCP1096 also offer the highest power rating of any 802.3bt device on the market. Typically, systems can only put in the rated power; 90 W in the case of 802.3bt for a worst case power delivery of 71.3 W. With the NCP1095 and NCP1096, systems can put in 100W (e.g. maximum power rating) so that the power delivered at the end of the cable is as close to 90 W as possible.
ON Semiconductor doesn’t offer just PoE interface controllers. They provide all of the surrounding components required to build world-class power systems. To accelerate design, ON Semiconductor also has complete reference designs for a wide range of applications, including switching power supplies, isolated/non-isolated LED drivers, security cameras, and more. These are full solutions, providing power, protection, and interconnectivity. Figure 4, for example, shows the block diagram for a smart lighting controller.
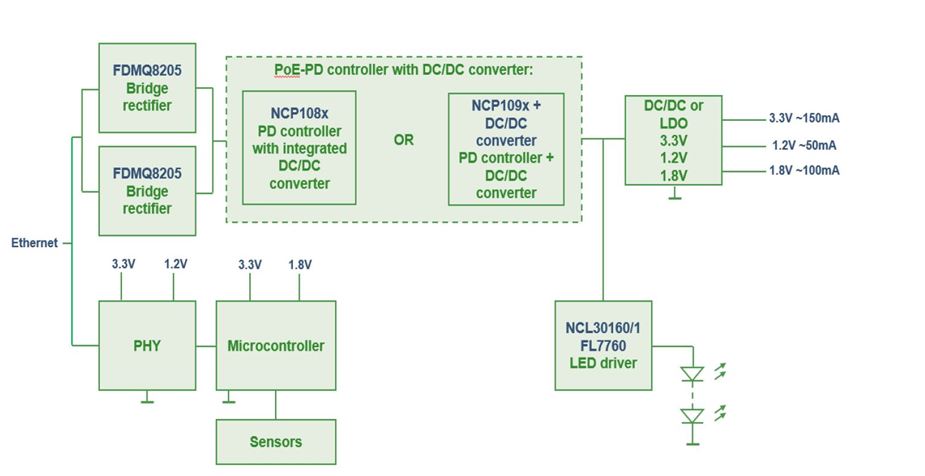
Figure 4: The block diagram for a smart lighting controller based on Power over Ethernet
To give developers a jumpstart on design, ON Semiconductor offers the NCP1095/NCP1096 Evaluation Board. This EVB not only enables developers to begin early design and prototyping, it provides a way to focus on power efficiency early in the design process. The EVB is itself a highly efficient design. For example, under worst case test conditions – class 8 full power of 71.3 W, operating at the lowest voltage of 41.1 VDC and highest current of powered device input of 1.73 A – the EVB operates at 99.20% efficiency.
802.3bt opens the way for a whole new class of applications, including smart buildings, industrial equipment, and lighting applications. With 90 W capabilities, 802.3bt sets a new standard in the industry for connected power delivery. Designers can now deploy high powered devices with greater flexibility, leading to more reliable and cost-effective infrastructure.
______________________________________________
1 “Power over Ethernet – Cable Losses”, Ethernet Alliance, June 2017
2 “Power over Ethernet – Cable Losses”, Ethernet Alliance, June 2017

